Advanced Insights
Advanced insights allow business analysts to deep-dive into the data collected by Viva Insights. For example, analysts can write custom queries to explore meeting metrics or other quantitative datasets.
Advanced Insights
To learn more about Advanced insights features, please see https://learn.microsoft.
com/en-us/viva/insights/advanced/introduction-to-advanced-insights.
Viva Insights has its own role, Viva Insights admin. With this role, an admin can assign licenses and manage insights settings. A Teams admin role is required to publish Viva Insights to Teams.
Describe the Capabilities of the Microsoft 365 Admin Center and Microsoft 365 User Portal
Microsoft 365 has a number of portals and web interfaces used for everything from administration to the end-user experience. In this section, you’ll briefly look at the capabilities of Microsoft 365 both from the administrative and end-user sides.
Microsoft 365 Admin Center
With the Microsoft 365 admin center, you can conveniently perform a range of tasks, such as resetting passwords, viewing invoices, adding or removing users, and much more.
Here’s how to get started:
- Sign in to the Microsoft 365 admin center (https://admin.microsoft.com) using an account with an administrative role assigned.
2. At the top of the admin center, you’ll see a list of top actions recommended for you. These actions may vary based on the previous setup actions taken, such as creating new accounts, utilizing Teams, configuring email settings, or installing Office apps. SeeFigure 6.2:
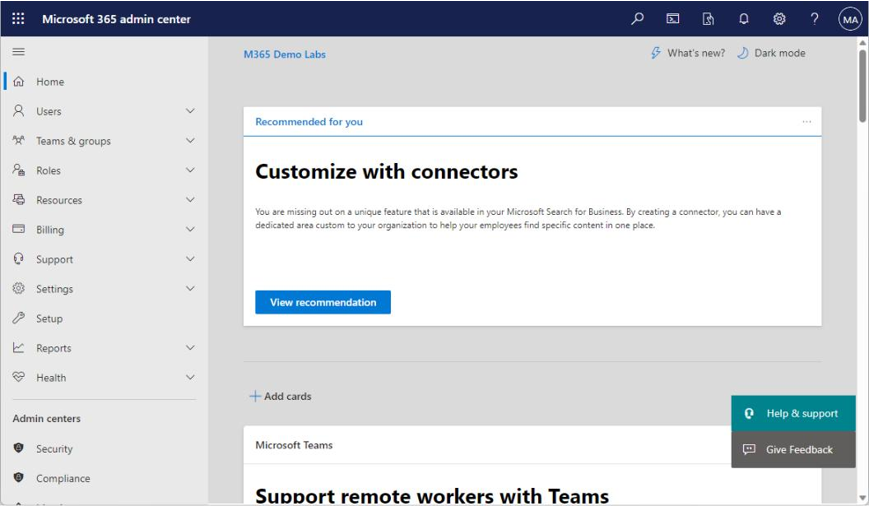
Figure 6.2 – Microsoft 365 admin center
Each of the navigation menu options has a variety of settings and actions you can take:
- Users: The Users menu has options for creating and managing users and contacts, as well as managing license assignments for users.
- Teams & groups: From this menu option, you can create a new team or manage existing ones. You have the option to manage team members and assign Teams collaboration policies. You can also manage shared mailboxes from this area.
- Roles: The Roles menu allows you to assign administrative roles (such as User administrator, Global administrator, Teams administrator, and so on) as well as to create and manage administrative units.
- Resources: The Resources menu option area can be used to provision non-person mailbox resources such as rooms and equipment and SharePoint sites.
- Billing: The Billing menu is where you can administer the subscriptions and licenses owned by your organization. Billing options also include starting product trials, assigning licensing, and updating payment methods.
- Support: From the Support menu, you can search documentation and open service requests with Microsoft.
- Settings: The Settings menu contains options for adding and removing domains from your Microsoft 365 tenant, viewing directory synchronization errors, managing Microsoft Edge sites and settings, managing org-wide settings such as calendar sharing and directory synchronization, and toggling the availability of several integrated Microsoft 365 apps.
- Setup: The Setup menu can be used to help provide configuration guidance and walk-throughs for a variety of scenarios and products.
- Reports: The Reports menu contains information about usage and statistics for the Microsoft 365 tenant.
- Health: The Health area can be used to get a view of the status of the entire Microsoft 365 service, including Windows releases, the Microsoft 365 service health, information from the message center regarding health or service updates, and network connectivity.
- Admin centers: Expanding the Admin centers menu exposes the most popular admin centers (Security, Compliance, Identity, Exchange, SharePoint, and Teams), as well as an All admin centers option. The All admin centers option has links to administrative interfaces for all products on the Microsoft 365 platform, as shown inFigure 6.3:
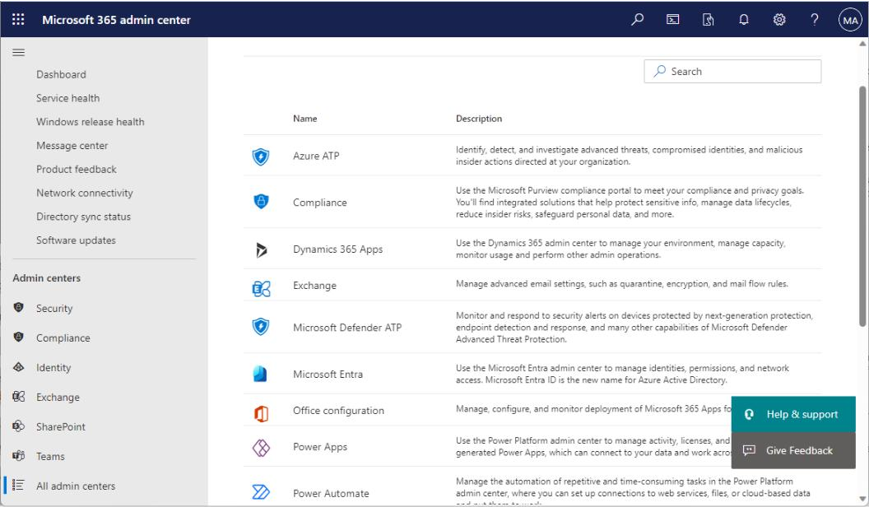
Figure 6.3 – All admin centers page
In addition to the admin components and help resources, the admin center also enables you to use
Azure Cloud Shell—a web-based shell interface for managing Microsoft 365, as shown inFigure 6.4:
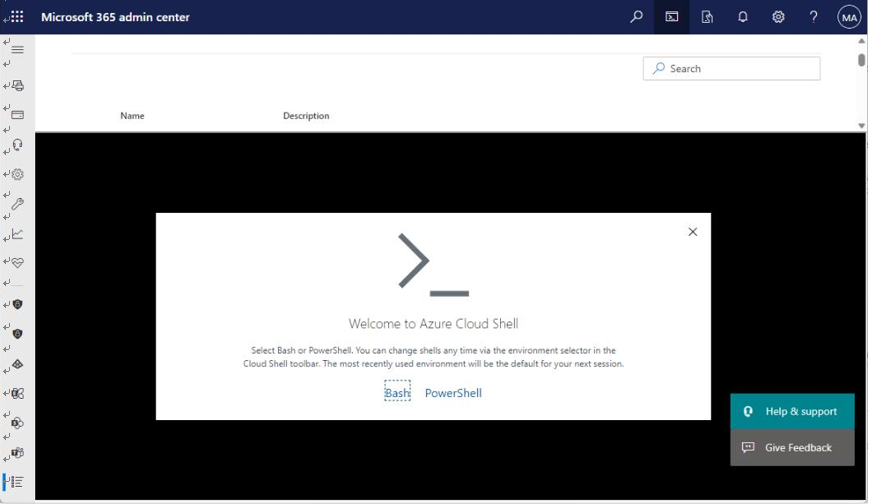
Figure 6.4 – Azure Cloud Shell
Launching Azure Cloud Shell requires access to an Azure subscription where a storage account can be created and used.