Document Storage
Although documents can be accessed from almost all the services of the suite, Microsoft 365 has three primary interfaces (listed next) where users can store, share, and collaborate on files:
- ODFB: Personal documents
- SPO sites: Team, group, or department documents
- Teams: Team, group, or department documents
The underlying storage component for all these interfaces is SPO. Documents stored in SPO (or any service that leverages SharePoint) are automatically indexed, support custom metadata, have versioning enabled, and can be synchronized between desktop and mobile devices. All locations are automatically covered under the organization’s security and compliance requirements.
Table 7.2 depicts the main differences between ODFB, SPO, and Teams for document storage:
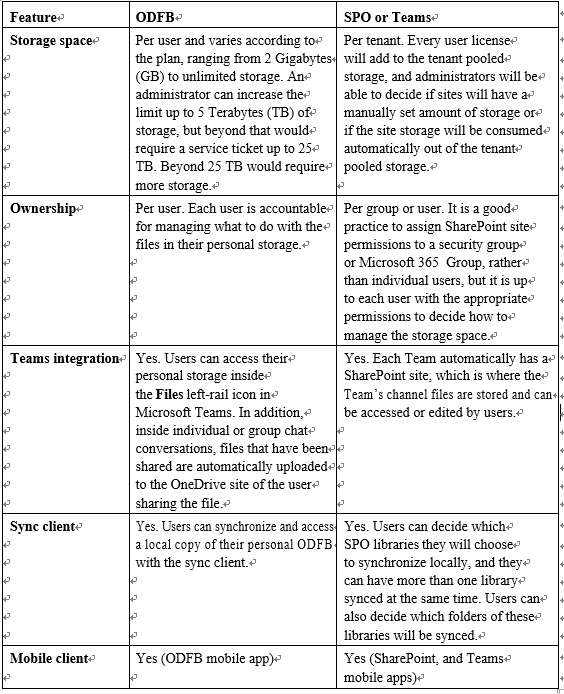
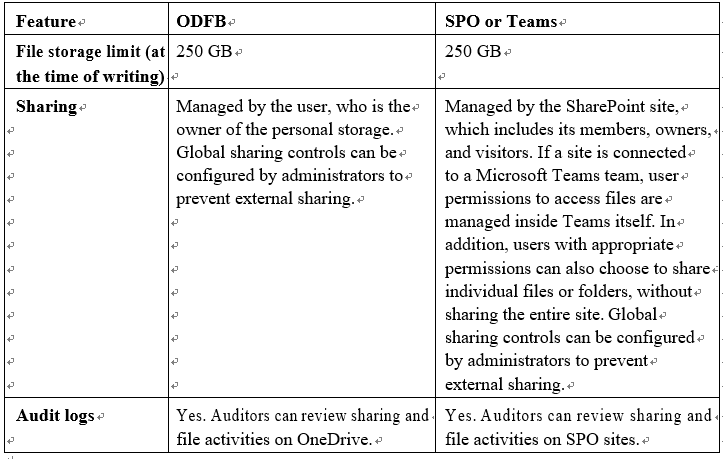
Table 7.2 – Storage locations, features, and capabilities of ODFB, SPO, and Teams
Sharing
Among the benefits of storing documents in OneDrive, SharePoint, or Teams is the ability to share files without needing to send a copy to each recipient. Efficient file sharing is also important because it allows organizations to manage access to content. Documents sent as email attachments may be outside the management or oversight of security, compliance, or business administrators. When shared inside the framework of ODFB, SharePoint, or Teams, files are kept in place and are configured so that users cannot send them to another party.